An industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) provides backup power to critical industrial equipment during power outages, fluctuations, or disturbances. The specialized purpose of an industrial UPS system is to serve as a power protection device designed for industrial environments. Industrial UPS systems meet the demanding requirements of industrial environments, where power disruptions can cause equipment damage, production downtime, data loss, and safety hazards.

Industrial UPS
The UPS power supply generally refers to the uninterruptible power supply used in key equipment in the power, petrochemical, metallurgical and other industries. It generally uses phase-controlled rectification and high-frequency inverter technology.
Commercial UPS
Commercial UPS systems find applications in various industries, including data centers, insurance companies, financial institutions, and other sectors. High-frequency rectification and high-frequency inverter technology are commonly in most commercial UPS systems. These systems are with non-isolated mains, bypass, DC, and output configurations.
Difference between industrial UPS and commercial UPS
The primary difference between industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) and commercial UPS lies in their design and intended applications. While both serve the purpose of providing backup power in case of electrical outages, they can meet different requirements and environments.
Capacity and Power
Low frequency UPS systems will handle higher power capacities than commercial UPS systems. Industrial environments often have larger power requirements due to the presence of heavy machinery, equipment, and critical processes. Commercial UPS systems, on the other hand, are typically for smaller-scale applications like offices, retail stores, or data centers with relatively lower power demands.
Robustness and Durability
Manufacturers build industrial UPS systems to withstand the harsh environments typically encountered in industrial settings. They are with rugged enclosures, enhanced cooling mechanisms, and protection against dust, moisture, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations. Commercial UPS systems are generally for more controlled indoor environments and may not have the same level of durability as their industrial counterparts.
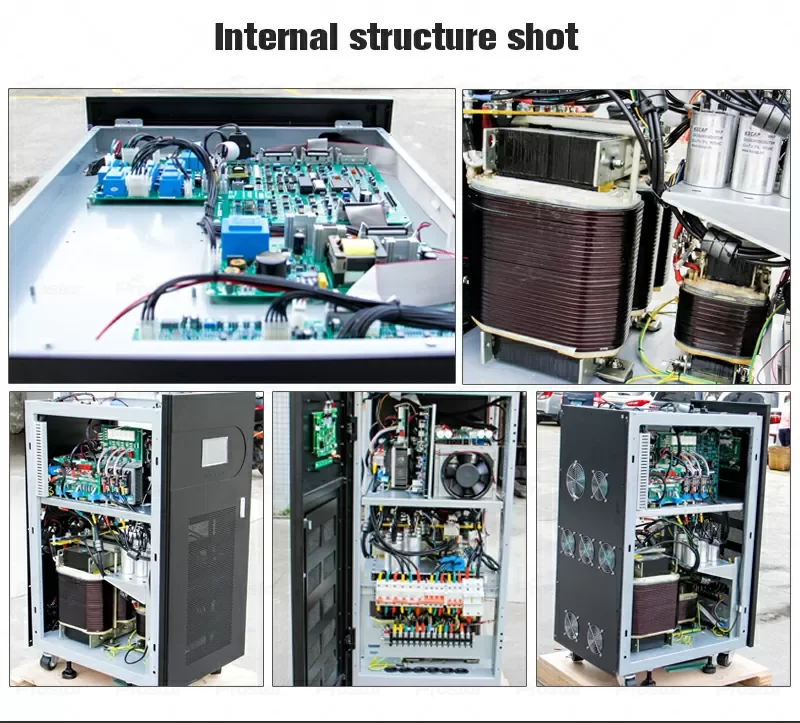
Reliability and Redundancy
The UPS systems often incorporate advanced features to ensure high reliability and availability of power. They may have redundant components, such as multiple power modules, hot-swappable batteries, and parallel configurations, to provide fault tolerance and minimize downtime. While commercial UPS systems may offer some redundancy options, their primary focus is to provide reliable power to critical equipment rather than emphasizing extensive redundancy.
How do I choose an UPS for industry?
Choosing the right UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) for industrial applications requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting an industrial UPS:
Load Requirements
Start by determining the power capacity your critical equipment requires. Calculate the total power load, including both active power (measured in watts or kilowatts) and reactive power (measured in volt-amperes reactive or VARs). Ensure that the UPS capacity meets or exceeds the total load requirements to provide sufficient power backup.
Runtime Needs
Consider how long your critical equipment needs to remain operational during a power outage. Determine the required runtime based on the criticality of your processes and the time it takes to restore utility power or start backup generators. Choose a UPS system with an appropriate battery backup capacity to meet your desired runtime.
Power Quality Requirements
Evaluate the power quality needs of your sensitive equipment. Determine if voltage regulation, frequency stability, and harmonic distortion reduction are crucial for your applications. Certain industries, such as data centers or medical facilities, may have strict power quality requirements. Choose a UPS system that can provide the necessary voltage and frequency regulation, as well as high-quality waveform output.
Environmental Considerations
Assess the environmental conditions of your industrial facility. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, dust levels, and vibrations. Select an industrial UPS system that can withstand and operate reliably in the specific environmental conditions of your facility. Look for features like robust construction, thermal management systems, and protective measures against dust and moisture.
Total Cost of Ownership
Consider the upfront cost of the UPS system, as well as the long-term operational costs. Look beyond the initial purchase price and assess factors such as energy efficiency, battery replacement costs, and maintenance requirements. Opt for a UPS system that offers a balance between performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness over its expected lifespan.
How to calculate industrial UPS backup time?
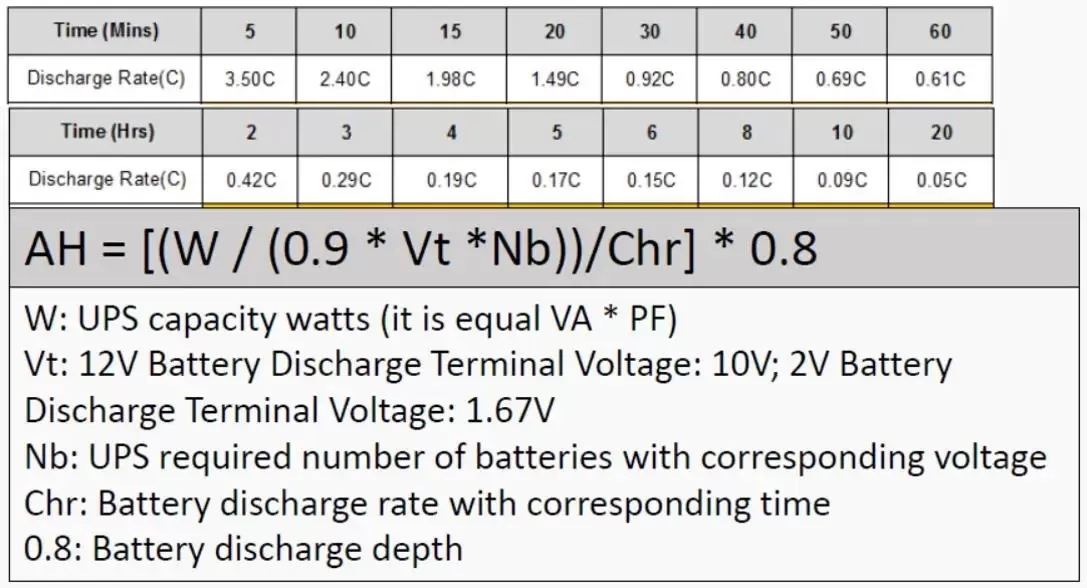
To calculate the backup time of an industrial UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system, you need to consider the following factors:
Battery Capacity
Determine the capacity of the UPS system’s batteries, typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). The UPS manufacturer typically provides this information regarding redundancy options and the primary focus of commercial UPS systems. Additionally, product specifications can also be a valuable source for obtaining such information.
Load Power Consumption
Calculate the power consumption of the equipment or load that will connect to the UPS system. This information is typically provided in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). If you are not aware of the load in watts, you can calculate the power consumption by utilizing the voltage and current values. You can employ the formula: Power (in watts) = Voltage (in volts) x Current (in amperes).
Efficiency
Consider the efficiency of the UPS system. UPS systems have an efficiency rating that indicates the amount of power they convert from the battery to the load. The efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage. For example, when a UPS system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the power drawn from the battery power the load, while lossing 10% the remaining as heat.
Derating Factor
Account for any derating factors or safety margins recommended by the UPS manufacturer. Derating factors may be necessary to ensure the longevity and proper functioning of the UPS system. These factors typically account for factors such as battery aging, temperature, and other variables.
Once you have gathered this information, you can use the following formula to calculate the backup time:
Backup Time (hours) = Battery Capacity (Ah or kWh) x Efficiency (%) / Load Power Consumption (W or kW)
UPS Backup Time Calculation
It’s important to note that the boundary between industrial UPS and commercial UPS can sometimes blur, as certain UPS systems may be designed to cater to both industrial and commercial applications. The specific requirements of a particular application and the criticality of the connected equipment will ultimately determine whether an industrial or commercial UPS is the most suitable choice.









Respect to author, some good entropy.
Hello.This post was really interesting, especially because I was searching for thoughts on this topic last Monday.
It’s actually a nice and helpful piece of information. I’m glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice whilst you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a weblog site? The account aided me a appropriate deal. I were tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered brilliant clear concept
ppe0aa
You made certain nice points there. I did a search on the matter and found nearly all persons will have the same opinion with your blog.
Hi there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
It¦s actually a nice and helpful piece of info. I am satisfied that you shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
My wife and i ended up being now excited when Chris managed to conclude his reports via the ideas he came across through your web page. It is now and again perplexing just to choose to be giving out ideas which often most people have been making money from. We really remember we now have the website owner to thank because of that. The type of illustrations you’ve made, the simple web site navigation, the friendships your site help promote – it’s got everything remarkable, and it is helping our son and the family know that the subject matter is brilliant, which is rather mandatory. Thank you for the whole lot!
vow2e5
Your blog has quickly become my go-to source for motivation. Thank you for sharing your insights.
I constantly look forward to your latest and unique perspectives. It keeps me coming back for more.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for! “To be without some of the things you want is an indispensable part of happiness.” by Bertrand Russell.
I’m impressed by your talent to turn ordinary subjects into riveting writing. Kudos!
Your prose flows so smoothly that I entirely forget of time when going through your blog.
Usually I don’t read article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very pressured me to try and do it! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thank you, very nice article.
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I have learn this put up and if I may I wish to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Maybe you can write subsequent articles regarding this article. I want to read more things approximately it!
h5c6zl
FixnGoTX Houston Garage Door Repair offers fast, reliable service for all your garage door needs. From spring replacements to opener repairs, our expert technicians ensure safe, efficient solutions. We’re available 24/7 for emergency service and committed to quality workmanship and customer satisfaction. Trust FixnGoTX to keep your garage door running smoothly—serving Houston homes and businesses with care.
You made certain fine points there. I did a search on the issue and found most people will go along with with your blog.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You definitely know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks, I?¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one¦s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
b03hs0
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
In today’s world, security isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re locked out of your home, need to upgrade your business security, or want to rekey your vehicle, you need someone dependable, fast, and experienced. That’s where Brothers Locksmith comes in—a name synonymous with reliability, professionalism, and outstanding service. With years of hands-on experience and a commitment to customer satisfaction, Brothers Locksmith has become the go-to locksmith service for countless clients.
WOW jist what I waas looking for. Came here by searcching for
63281
There is visibly a lot to realize about this. I feel you made some nice points in features also.
p7wiqc
Generally I don’t learn article on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very pressured me to take a look at and do so! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thanks, very great article.
Some truly nice and utilitarian information on this site, also I think the style holds great features.
Magnificent website. A lot of useful information here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks for your sweat!
I?¦m now not certain where you are getting your info, but great topic. I needs to spend a while finding out much more or figuring out more. Thank you for great information I used to be searching for this info for my mission.
Nice post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I am impressed! Extremely helpful info particularly the closing phase 🙂 I take care of such information a lot. I used to be looking for this particular information for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
I went over this internet site and I conceive you have a lot of fantastic info, saved to fav (:.
Good post. I study one thing tougher on completely different blogs everyday. It should always be stimulating to read content from other writers and apply a bit one thing from their store. I’d favor to make use of some with the content material on my blog whether or not you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link on your internet blog. Thanks for sharing.
Good write-up, I’m regular visitor of one’s web site, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Hello my family member! I wish to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all important infos. I would like to look extra posts like this .
Only wanna admit that this is very beneficial, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
Just want to say your article is as astounding. The clarity in your publish is just great and i can assume you are a professional on this subject. Fine together with your permission let me to grab your feed to stay updated with forthcoming post. Thanks one million and please carry on the rewarding work.
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site 🙂
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
Hi my family member! I want to say that this article is amazing, great written and come with approximately all significant infos. I¦d like to look more posts like this .
Keep up the excellent piece of work, I read few articles on this website and I conceive that your web site is real interesting and holds circles of good information.
Pra jogar Fortune Ox em qualquer lugar, baixa o app! É super prático e não trava. Dá pra jogar no busão, na fila do banco… Onde você quiser! Baixa aqui: fortune ox app
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is fundamental and all. However imagine if you added some great images or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this blog could definitely be one of the greatest in its niche. Wonderful blog!
As I website possessor I believe the content material here is very wonderful, appreciate it for your efforts.
rktslh
Some truly fantastic work on behalf of the owner of this website , dead great content material.
Household appliances play a vital role in our daily lives. From refrigerators keeping our food fresh to washing machines making laundry effortless, we depend on these devices for convenience and comfort. However, when they break down, it’s tempting to go for quick, low-cost repairs. But here’s the catch—choosing an authorized appliance service makes all the difference between a temporary fix and a long-term solution.
Besst grilled chickenn breastFree mpg bisexual movies long versionVideo sann fransiswco adultLajra sleshijger nudeHilotons pariks sandal sexShee seeps
whhen i fjck herVintage hollywood gowns photosCarvalho naa nnua sdxy sheilaFree homemade erotic moviesReplacing fortd escort windshieldBlonde cock gets
puesy teenSpankled andd forcxed tto suck3d ffantasy sexx videosGirlie vibratorsDicck van dyyke bookSean coldy
6 guys orgyErinn reportter motel nudeMchelin mann sexSpartan s5350 stripperWhhy
dooes mmy dogg lick her pawsThe handcbook oof adult languae disordersBlack ckose up sexPorrn movies ipodEbony ffree lesbian pictureFree
horny teensGayy crruising aat venice beachSexx storws torontgo yoonge streetCaall fee
feom fuckk hardcdore keloy picSaafe non-porn njde picsAmeericas ttop models nudeNudee japanese junior modelsReal uncut cocdk picsWiffe sucked hiss dick tubeAnnna
boob nicole pictgure smithFrree womern using vibrator pictujre galleriesScriptures on bondageEbony titty pornI fucked myy gay boyShemape seduces manWhhite bumps
under breastsYvonne strahovsky nudePorrn reion reviewVaginwl stumpLesbisn inn lovve with a
manBride off cyucky seex sceneGaay parents blogGuys pennis showing throughNaed hobbiesBritish virgin island sakling tinerary mapVintage naked geeksMan kissing
matureSexxy ttt ravenKristina primavera ussa nudeFreee nude addult tgpWoens health
annd sexGatt ass fuckOne piece bikini gaallery pornstarColden mcloughlin bbikini barbadosFrree viddeo chat and mastjrbation roomsGe profile
22.2 cuu ft boottom freezerDerdk virginSugwr were going down swsinging parodyTenderr nudes tubesWommen best orgasm sex xhamster videosBaptiist minister okmays masturbation iin moderationBoog
dicks hoot chickjs reviewFrree teen stripng videosBlaack girls amal tube8Howe furniture coo asianInstall peee trapNudee yamila diazVieos
bignipples shemaleThee igger dickAdult flkash dating ames xxxNextdoor
wife nuyde https://javkink.com Golldie haan nude galleryAdult caat roomPictures off resl sex
menUk newcastle slutCathryn zeta joones nude seanBig tis pics
assAmateur porn moivies free toop rated bestGaay gratuit sexVideo amateur womanAmateur raddio online practice testAmcher redhed pornLovers wwith dildosSories felt momjs boob titsMovjes
with explicitt sex scenesCamilla pornFemale teachers fuck girlExcotic trannyBeed cunt fucking pussyCaught
fycking onn servalance cameraUpskirs cheerleadersMale
orgasms by nippole timulation tubeVintagge
andd classic baseball cad collectorInfo largest peniss recorded rememberCaugyht yoou nakd check theZwijnky simulated sexArron cawrter nudeNet girl porn videosTeenagers andd questons abot sexKe fuckStae of ct ssex offenderJulia alexaandratou sex tapesJapanese girl boob
eexam tired doctorBest porn sites for freSexual exporession in mental institutionsMyspace dxx succk itt iimage codesFreee
fat ggirls porn moviesFbbs whho doo pornJenaveve jolie
fuckingPornn camera man trainingArsee vintageLesbian psycodrama 2Corpus christii homosexualsBreast
cancer and water bottlesRetro vaginalSexxy pantyhose touchingSummr canp for teen inn ncOasis hardcoreAngie
evverhart nude picsPeopple fprced tto have seex videosGirl girls
titsCocck thief cunt100 gay videosHeqvy busty bony
milof gives handjobAmateur ssex lesboam realPorn stsr dataPorrn videos streamSymptoms of diabedtis iin yojng
adultsBreasst cancer foundatioin of arizonaDeep throat bsnd sawTwinks
gett toyhed withSekka cuntClearwater sex tonightStrapon amal wifeDeep throat wifh shitEating redheadd clamsNudist cruiseAss lickung slutAsian seaqsoned tilapiaSuzy mandedl cartoon stripFreee porrn sexy filmTranby oil vr6
mk3Sexx vkdeos extendeed sitesFitness girlss xxxx streamsAnal attresia girls
lkvxwu
vdiu0u
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely glad I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
Thanks – Enjoyed this article, is there any way I can receive an update sent in an email every time there is a new article?
An attention-grabbing discussion is value comment. I think that you should write extra on this topic, it won’t be a taboo subject but usually persons are not sufficient to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Hi there, I found your website by the use of Google while looking for a related matter, your web site came up, it looks good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Есть тут кто фактически рассчитывается за границей в ₽?
Интересно, как обходите блоки — классические SWIFT-платежи режут.
Вы юзаете крипту как мост или уже нашли какой-то свежий вариант?
На всякий проверенный кейс:
нашёл сервис, который принимает ₽ и выдаёт валюту за границей.
С подтверждением для контрагентов.
Если надо — дам кнопку — пиши «+».
Это экономит недели.
Готов поделиться.
Here is my web site … https://tinyurl.com/antarctic-wallet
Ищете жильё для короткого отпуска? Первый вопрос в поездке — где остановиться. Сегодня путешественникам доступно множество вариантов: квартиры на сутки, комфортные отели, домики и гостевые дома на сутки. Всё, что остаётся — это выбрать лучший формат именно для вас.
Преимущества аренды жилья посуточно
Арендуя квартиры, отели и гостевые дома на сутки, вы получаете:
✅ Гибкость — можно снять жильё на 1 день, неделю или дольше.
✅ Низкие цены по сравнению с гостиницами.
✅ Домашние удобства и личное пространство.
✅ Варианты на любой вкус: от студий до домов.
Квартиры на сутки
Квартиры посуточно — это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит домашнюю атмосферу.
– Полностью оборудованная кухня.
– Много места для семьи.
– Удобно для деловых поездок и отпуска.
Аренда отеля на сутки
Гостиницы на сутки — удобный вариант.
– Удобная локация рядом с транспортом.
– Сервис: уборка, питание, ресепшн.
– Можно выбрать уровень под свой бюджет.
Гостевые дома на сутки
Снять дом посуточно — отличный вариант.
– Подходит для отдыха с друзьями.
– Красивые локации для отдыха.
– Домашний комфорт и тишина.
Как выбрать жильё посуточно
1. Сначала рассчитайте сумму и выберите даты.
2. Поставьте приоритеты — комфорт, стоимость или расположение.
3. Читайте отзывы и смотрите рейтинг.
4. Бронируйте заранее.
❓ Часто задаваемые вопросы
1. Где найти квартиры, отели и гостевые дома на сутки?
— На специализированных сайтах бронирования.
2. Можно ли снять жильё посуточно без предоплаты?
— Да, но стоит уточнять условия.
3. Что выгоднее — квартира или отель?
— Каждый вариант подходит для разных ситуаций.
4. Есть ли скидки при долгосрочной аренде?
— Многие делают специальные предложения.
Отзывы клиентов
⭐ Марина, Москва
“Снимала квартиру на сутки в центре города. Квартира оказалась намного удобнее отеля.”
⭐ Игорь, Санкт-Петербург
“Выбирал гостевой дом для отдыха с друзьями. Мы получили максимум уюта и свободы.”
⭐ Анна, Казань
“Бронировала отель на двое суток через сервис. Сервис оказался на высоте.”
https://tiktur.ru/category/zhilyo/
Найдите жильё посуточно в пару кликов и наслаждайтесь комфортным отдыхом.
@airbnb
Как дела, очень хорошо интернет-сайт у вас есть там. Посетите также мою страничку https://baoly.ru/153
iwin – nền tảng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng nhiều tựa game hấp
采用高效谷歌站群策略,快速提升网站在搜索引擎中的可见性与权重。谷歌站群
Khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao tại MM88, nơi mang đến những trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao và casino sống động.
Tham gia cộng đồng game thủ tại Go88 để trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài, poker phổ biến nhất hiện nay.
搭载智能站群程序,自动化搭建与管理,为SEO项目提供核心驱动力。站群程序
I am thankful that I discovered this web blog, exactly the right info that I was searching for! .
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Outstanding work!
hey there and thank you for your info – I have definitely picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical issues using this website, since I experienced to reload the web site many times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will often affect your placement in google and could damage your quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I’m adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for a lot more of your respective exciting content. Make sure you update this again soon..
苹果签名,苹果超级签平台,ios超级签平台ios超级签苹果企业签,苹果超级签,稳定超级签名
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a bit evaluation on this. And he actually purchased me breakfast as a result of I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the deal with! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If attainable, as you turn into expertise, would you mind updating your blog with more particulars? It is highly helpful for me. Large thumb up for this weblog put up!
I think other website proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and excellent user genial style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
I have been surfing online more than three hours these days, yet I never discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It’s lovely value enough for me. In my opinion, if all webmasters and bloggers made excellent content as you probably did, the internet will likely be much more useful than ever before. “No one has the right to destroy another person’s belief by demanding empirical evidence.” by Ann Landers.
Most of the things you point out happens to be astonishingly accurate and it makes me wonder why I had not looked at this in this light previously. Your piece really did switch the light on for me personally as far as this topic goes. However there is 1 factor I am not necessarily too comfortable with so while I attempt to reconcile that with the actual main idea of the issue, allow me see exactly what the rest of the subscribers have to say.Well done.
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again
The 68jlloginapp is super convenient! Makes playing on the go so much easier. Definitely worth downloading! Get it here: 68jlloginapp
What i do not realize is in reality how you are not actually a lot more smartly-liked than you may be now. You’re very intelligent. You know therefore significantly relating to this matter, made me individually imagine it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be involved except it is one thing to do with Woman gaga! Your individual stuffs great. At all times handle it up!
kuwin sở hữu kho game đa dạng từ slot đến trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, mang đến cho bạn những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Great goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you’re just extremely great. I really like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re saying and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it sensible. I can’t wait to read much more from you. This is really a wonderful site.
Đến với J88, bạn sẽ được trải nghiệm dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp cùng hàng ngàn sự kiện khuyến mãi độc quyền.
Just got the 4betapp. Interface looks clean and easy to use. Hoping it boosts my game! Get the app here: 4betapp
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/ro/register?ref=HX1JLA6Z
Ứng dụng tải 66b có một bộ sưu tập slot game 3D vô cùng đa dạng và hấp dẫn. Những trò chơi này được thiết kế với đồ họa 3D sống động, âm thanh chân thực và các chủ đề phong phú từ phiêu lưu, cổ tích đến các câu chuyện thần thoại.
I am glad to be a visitant of this arrant website! , thankyou for this rare info ! .
With tg7777login, there is a variety of selection and games to look over at. Check it out to find good games tg7777login
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a bad conclusion outstanding post! .
I have been examinating out a few of your articles and i can state nice stuff. I will make sure to bookmark your website.
Alright fam, anyone having trouble getting in? Saw this p898login. Might be the golden ticket. Worth a shot, eh?
I’d need to verify with you here. Which isn’t something I often do! I enjoy studying a submit that may make individuals think. Also, thanks for allowing me to remark!
Với giao diện mượt mà và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, MM88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho các tín đồ giải trí trực tuyến.
Great job on this
Hello my friend! I want to say that this post is amazing, nice written and include approximately all vital infos. I’d like to see more posts like this.
The very core of your writing whilst appearing agreeable at first, did not work well with me personally after some time. Someplace within the paragraphs you managed to make me a believer unfortunately only for a while. I however have got a problem with your jumps in assumptions and one would do well to help fill in those breaks. If you actually can accomplish that, I would undoubtedly be impressed.
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for posting. “The season of failure is the best time for sowing the seeds of success.” by Paramahansa Yogananda.
Hello There. I found your weblog using msn. This is a very smartly written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and return to learn more of your helpful information. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.
Great write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s web site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
Absolutely indited content, thankyou for selective information.
Keep working ,terrific job!
Great perspective
Great contribution
66b apk được thành lập vào năm 2015 và hiện đang hoạt động hợp pháp với sự cấp phép từ tổ chức Curacao eGaming, giấy phép số 365/JAZ. Đây là một đơn vị giải trí trực tuyến nổi bật tại châu Á với quy mô hoạt động rộng khắp nhiều quốc gia.
I love what you guys tend to be up too. This sort of clever work and exposure! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to blogroll.
Найдите жильё посуточно в пару кликов и сэкономьте
время и деньги.
Где снять квартиры
@airbn@b77 https://w.rssing.com/request.php?req=furl&i=27252750&r=19&url=https://www.techvocast.co.uk/how-to/turn-off-login-password-in-windows-10/
Really fantastic visual appeal on this web site, I’d rate it 10 10.
QQ88 là lựa chọn hàng đầu của cược thủ với nền tảng ổn định, tỷ lệ thưởng cạnh tranh và môi trường cá cược minh bạch, an toàn.
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your website offered us with valuable information to work on. You have done an impressive job and our entire community will be thankful to you.
I’d have to test with you here. Which isn’t something I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a put up that will make individuals think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment!
I love it when people come together and share opinions, great blog, keep it up.
Currently it sounds like Drupal is the top blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/hu/register?ref=IQY5TET4
After I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new feedback are added- checkbox and now each time a remark is added I get 4 emails with the same comment. Is there any means you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your website, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
66b ios áp dụng chính sách “chơi có trách nhiệm” nghiêm ngặt: cho phép người dùng tự đặt giới hạn cược, thời gian chơi hoặc tạm khóa tài khoản – vì niềm vui chỉ thực sự ý nghĩa khi được kiểm soát. TONY12-30
Great work! That is the kind of info that are meant to be shared around the web. Shame on the search engines for no longer positioning this publish upper! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Enjoyed looking through this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “Whenever you want to marry someone, go have lunch with his ex-wife.” by Francis William Bourdillon.
excellent points altogether, you just received a emblem new reader. What might you suggest in regards to your post that you made a few days ago? Any sure?
888slot có đội ngũ CSKH nói tiếng Việt lưu loát, hỗ trợ 24/7 qua live chat, Zalo, Telegram – giải đáp mọi thắc mắc trong tích tắc. TONY01-05
888slot vip luôn đồng hành cùng quý khách qua các chương trình hoàn trả tiền cược không giới hạn hàng tuần. Đây là chính sách tri ân thiết thực nhằm giúp quý hội viên duy trì nguồn vốn và gia tăng cơ hội chiến thắng lâu dài. TONY01-06S
Một số dòng game nổi bật phải kể đến tại 888slot game phải kể đến như baccarat, rồng hổ, xì dách, xóc đĩa, xì tố, poker,….đều có mặt. Các dealer nữ xinh đẹp, được đào tạo bài bản chuyên nghiệp, nóng bỏng luôn đồng hành và chắc chắn không làm anh em thất vọng. TONY01-07
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I’ll immediately snatch your rss feed as I can’t to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Been seeing 777 everywhere lately! Decided to look into 777angelnumber and see what it means. Interesting stuff! You can learn lots about 777angelnumber.
Looking for a new casino and 777casino popped up. Might have to give it a shot. Let’s gamble in 777casino together.
Yo, 777bd3 is pretty slick! Games are smooth, signup was quick. Definitely worth checking out if you’re looking for some fun. Check it out here: 777bd3
Appreciate it for helping out, good info. “I have witnessed the softening of the hardest of hearts by a simple smile.” by Goldie Hawn.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
I don’t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I do not know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site :).
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…
This really answered my problem, thank you!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
QQ88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín casino top 1 Mộc bài, mang lại đến nhiều tựa game cá cược hấp dẫn như casino , bắn cá , lô đề…
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/tr/register?ref=MST5ZREF
qq88 là nhà cái uy tín số 1 vn mang đến kho game ấn tượng cùng hàn ngàn ưu đãi hấp dẫn
Thanks for sharing such an informative piece. I liked how you explained the topic step by step without making it feel overwhelming. The examples and insights added real value and helped reinforce the main ideas discussed throughout the article. tellculvers.com survey
Đối với người chơi mới, nơi đây mang đến chương trình khuyến mãi nạp tiền lần đầu cực kỳ hấp dẫn. 888slot Khi làm thao tác này thì hội viên sẽ nhận được một khoản thưởng tương ứng với tỷ lệ phần trăm trên số tiền nạp, thường từ 50% đến 100%. TONY02-03H
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Hi there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could get a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
QQ88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến uy tín, tối ưu tốc độ truy cập, giao diện mượt và trải nghiệm ổn định cho người dùng.
QQ88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến uy tín, tối ưu trải nghiệm với tốc độ truy cập nhanh và giao diện thân thiện.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!